Subtitle
Disease and toxicity outcomes for a modern cohort of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of cutaneous origin involving the parotid gland: Comparison of volumetric modulated arc therapy and pencil beam scanning proton therapy.
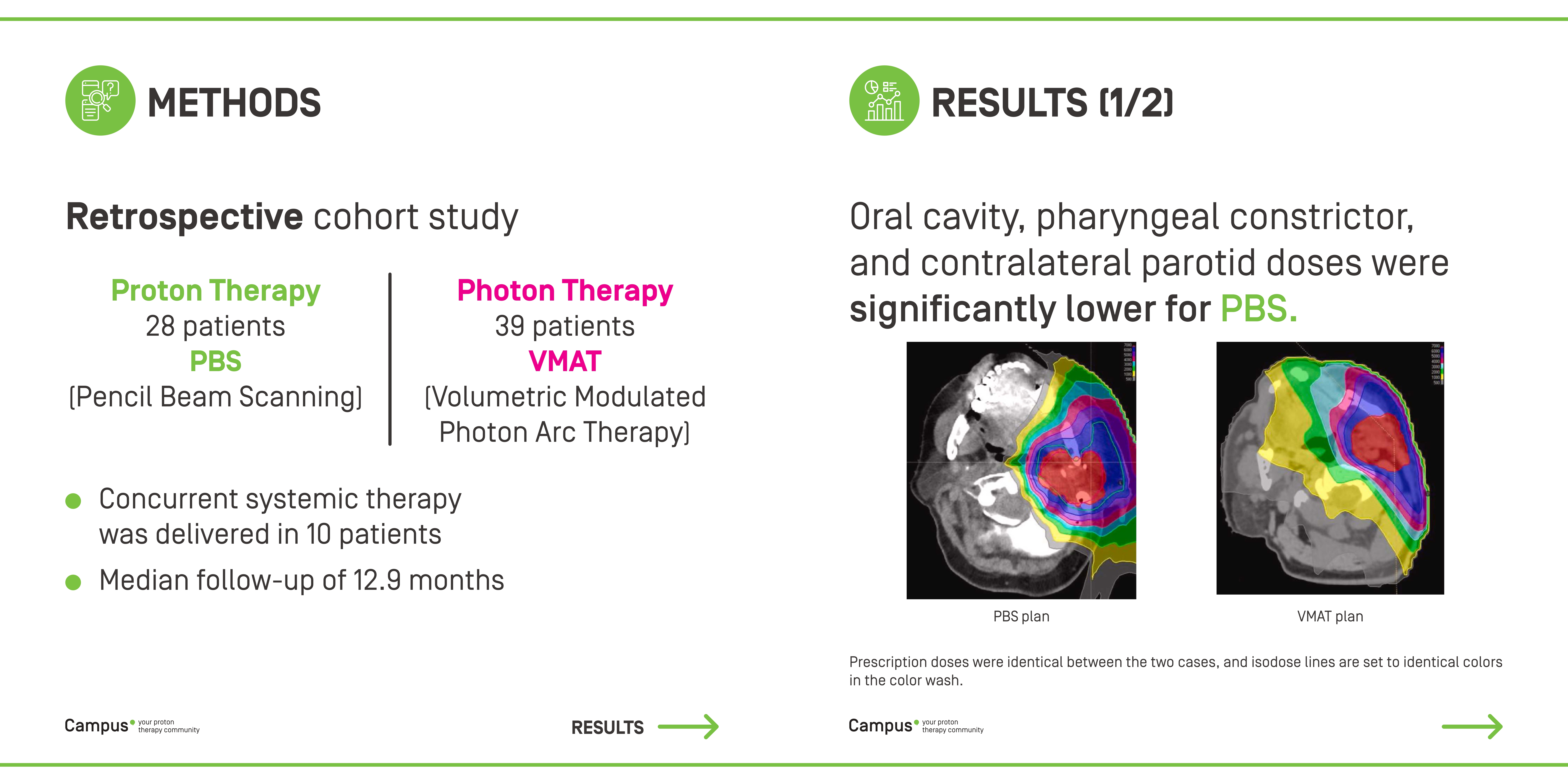
Published in the Green Journal, this study reported early results of 67 patients with cutaneous SCC involving parotid gland treated with VMAT (n=39, 58.2 %) and PBT (n=28, 41.8 %). This study reported significantly lower dose to oral cavity, pharyngeal constrictor, and contralateral parotid doses achieved by PBT compared to VMAT, which translated to reduction in early toxicity. Median weight change was -3.8 kg for VMAT and -3 kg for PBT (p = 0.013). Lower rates of ≥ grade 1 xerostomia (p = 0.002) and ≥ grade 1 dysguesia (p < 0.001) were demonstrated with PBT.